Glaucoma is a medical condition resulting in damage to the optic nerve potentially leading to severe vision loss or blindness. It is frequently associated with abnormally elevated pressure within the eyes. The optical nerve is responsible for transmitting vision signals from the eye to the brain, thereby allowing you to see clearly. When the optic nerve is damaged from glaucoma you may suffer from severe or complete vision loss. Glaucoma is one of the leading (and irreversible) causes of blindness in adults over 60 years of age.
What is Glaucoma?

Symptoms of Glaucoma:
- Patchy blind spots in the central or peripheral vision
- Patchy blind spots in both eyes together
- Tunnel vision and the loss of peripheral vision
- Severe headaches
- Eye pain
- Halos around lights
- Redness in the eyes
- Blurred vision
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blindness in one or both eyes (if left untreated)
Causes of Glaucoma
Glaucoma occurs when the optic nerve is damaged. As the optic nerve gradually deteriorates in health, the blind spots in your central and peripheral vision gradually increase. Many cases of glaucoma occur because of increased pressure in the eyes, which directly contributes to the deterioration of the optic nerve. As such, to understand the true cause of glaucoma, the eye doctor investigates the possible causes of increased pressure in your eyes.
You may suffer from increased eye pressure because of the buildup of the aqueous humor, a fluid that flows within the eyes. The aqueous humor usually drains out through the intersection where the iris and cornea meet. But if you have excess aqueous humor or the drainage system malfunctions, the fluid may accumulate within the eyes, leading to an increased risk of high eye pressure and glaucoma.
There are various types of glaucoma, such as open-angle glaucoma, angle-closure glaucoma, normal-tension glaucoma, glaucoma in children, pseudoexfoliation glaucoma, and pigmentary glaucoma. The specific root cause of each type of glaucoma is different. Your eye doctor will perform numerous tests to identify the specific type of glaucoma, diagnose its root cause, and formulate a personalized treatment plan for you. A comprehensive eye examination is essential to protect the health of your eyes and maintain your vision.
The Diagnosis & Treatment of Glaucoma
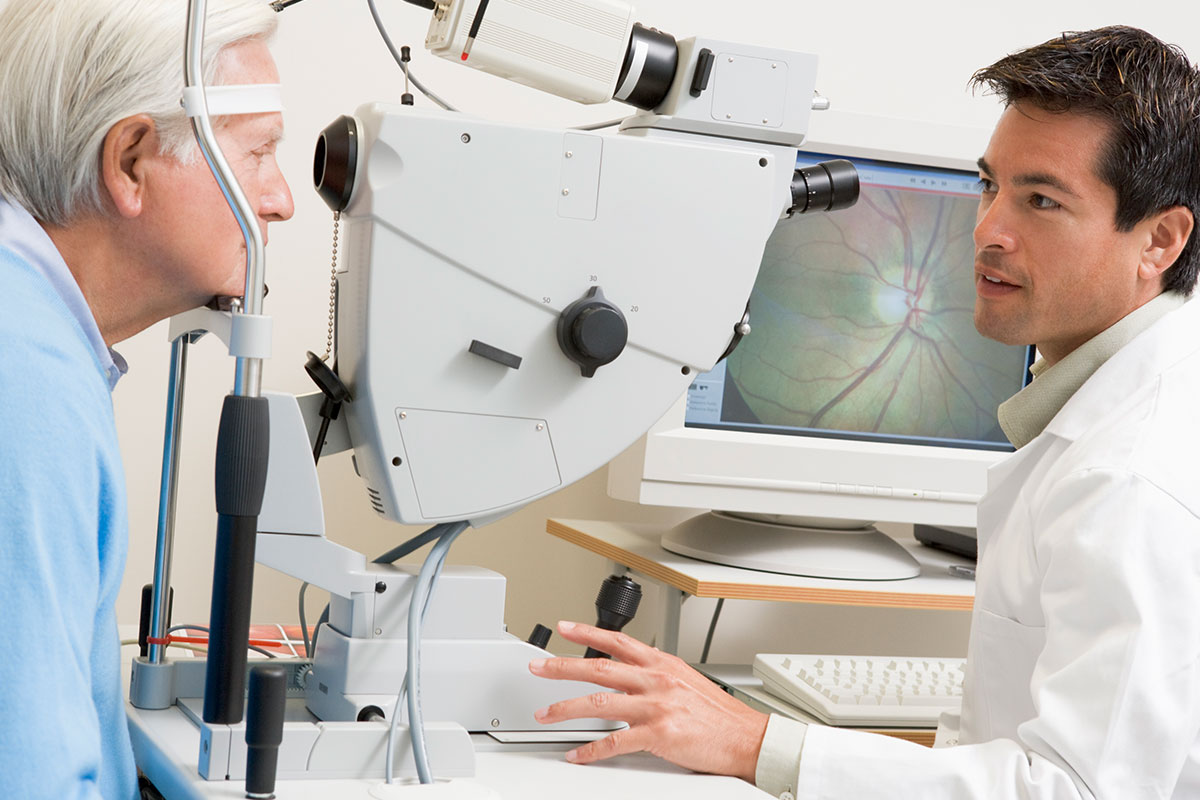
During your eye examination, your ophthalmologist will review your medical history, examine your eyes, discuss your symptoms, and recommend a series of glaucoma imaging tests. The eye doctor will measure the intraocular pressure (tonometry), check for vision loss (visual field test), measure the corneal thickness (pachymetry), and examine the drainage angle (gonioscopy), and test the optic nerve for damage. After a thorough evaluation, the eye doctor will formulate a personalized treatment plan.
The vision loss caused by glaucoma can’t be reversed, but the eye doctor can prevent further loss of vision or slow down the progression. The eye doctor will treat glaucoma by lowering the intraocular pressure, which may include administering prescription eye drops, oral medications, or laser treatments. In some cases, the eye doctor may need to perform surgery in an operating room to improve the drainage of the aqueous humor fluid.
If you notice the signs and symptoms of glaucoma, you must contact your ophthalmologist to explore your treatment options. Our eye doctors always recommend the least invasive solutions possible, and we only recommend surgical intervention when absolutely necessary.
Schedule an Appointment
Medical Surgical Eye Institute is a premier eye care center specializing in the latest diagnostic solutions and treatments for eye conditions. Our medical providers perform a thorough evaluation to understand the root cause of your eye conditions and formulate a personalized treatment plan. Since vision loss due to glaucoma is irreversible, we encourage you to schedule regular eye exams to diagnose and treat eye pressure changes at the earliest stage possible. Please schedule an appointment for your eye exam in Worcester, MA.

